-
Feed de Notícias
- ECOSYSTEM
- EXPLORAR
-
Páginas
-
Grupos
-
Eventos
-
Blogs
IoT Sensors: The Foundation of a Smarter, Connected World
🌐 IoT Sensors: The Foundation of a Smarter, Connected World
The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed how we live, work, and interact with technology — and at the core of this transformation are IoT sensors. These small but powerful devices act as the “eyes and ears” of connected systems, capturing valuable data from the physical world and translating it into actionable insights.
🔍 What Are IoT Sensors?
IoT sensors are devices that detect and measure changes in their environment — such as temperature, pressure, humidity, motion, light, or proximity — and transmit that data to a network for analysis. When integrated into IoT systems, they enable real-time monitoring, automation, and data-driven decision-making.
The beauty of IoT sensors lies in their versatility. From wearable health monitors to smart city infrastructure and industrial automation, sensors provide the data needed to optimize performance, improve safety, and enhance efficiency across multiple domains.
𝐃𝐨𝐰𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐝 𝐏𝐝𝐟 𝐁𝐫𝐨𝐜𝐡𝐮𝐫𝐞 — https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=26520972
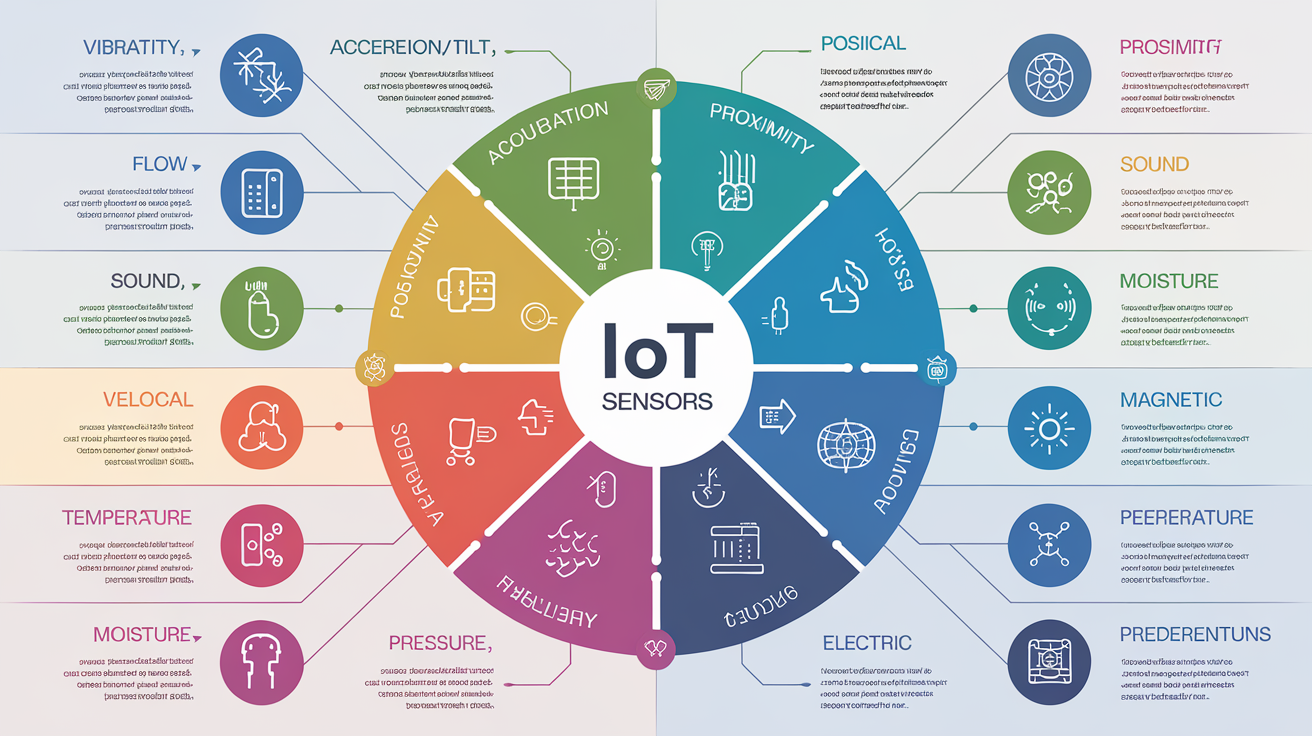
⚙️ Key Types of IoT Sensors
- Temperature Sensors: Monitor heat levels in manufacturing, logistics, and smart homes.
- Proximity Sensors: Detect the presence or absence of nearby objects — widely used in retail and robotics.
- Pressure Sensors: Measure fluid or air pressure in automotive and industrial equipment.
- Gas Sensors: Ensure air quality and detect hazardous leaks in industrial settings.
- Motion Sensors: Enable automation in lighting, security, and smart appliances.
- Image and Optical Sensors: Power vision systems in drones, vehicles, and surveillance cameras.
🌎 Applications Across Industries
IoT sensors have become the backbone of digital transformation in virtually every sector:
- Smart Manufacturing: Sensors track equipment performance, detect faults early, and support predictive maintenance — minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
Healthcare: Wearable sensors continuously monitor vital signs, enabling remote patient care and proactive health management.
- Agriculture: Soil and weather sensors provide data for precision farming, improving crop yields while reducing resource waste.
- Smart Cities: Sensors collect data on traffic, waste, lighting, and air quality to create safer, more efficient urban environments.
- Energy and Utilities: Smart grids use IoT sensors to monitor consumption patterns, detect outages, and optimize energy distribution.
🚀 The Future of IoT Sensors
As industries continue to digitize, the role of IoT sensors will only become more critical. From smart factories to connected healthcare ecosystems and sustainable cities, sensors are driving innovation across the global landscape.
By combining IoT sensors with artificial intelligence and advanced analytics, we are entering an era where data doesn’t just inform decisions — it transforms how systems operate, adapt, and evolve.
IoT sensors are not just enabling connectivity — they are shaping the intelligent future of our world. 🌍
#IoTSensors #InternetOfThings #SmartTechnology #DigitalTransformation #SmartCities #AI #EdgeComputing #Industry40 #Innovation #Automation
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jogos
- Gardening
- Health
- Início
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Outro
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


